NeoAxis Levels |
NeoAxis Levels
NeoAxis Levels is a system which represent a set of techniques and tools to give the ability to get maximum rendering performance from modern GPUs. This is a complex system, consisting of many different techniques that are put together uniquely, we did a lot of research and creative work in order to get the system.
One of the key components of the system is the virtualized geometry technique, we call it Voxel LOD. The technique allows you to get the best rendering performance at far distances from the camera.
Screenshots below are made from "Samples\Starter Content\Scenes\Levels.scene" and City Demo.




Levels is based on a system of smooth levels of detail, each level of which can be implemented in a special way. Due to the smooth transition between levels, there is no great requirement for the visual identity of neighboring levels.
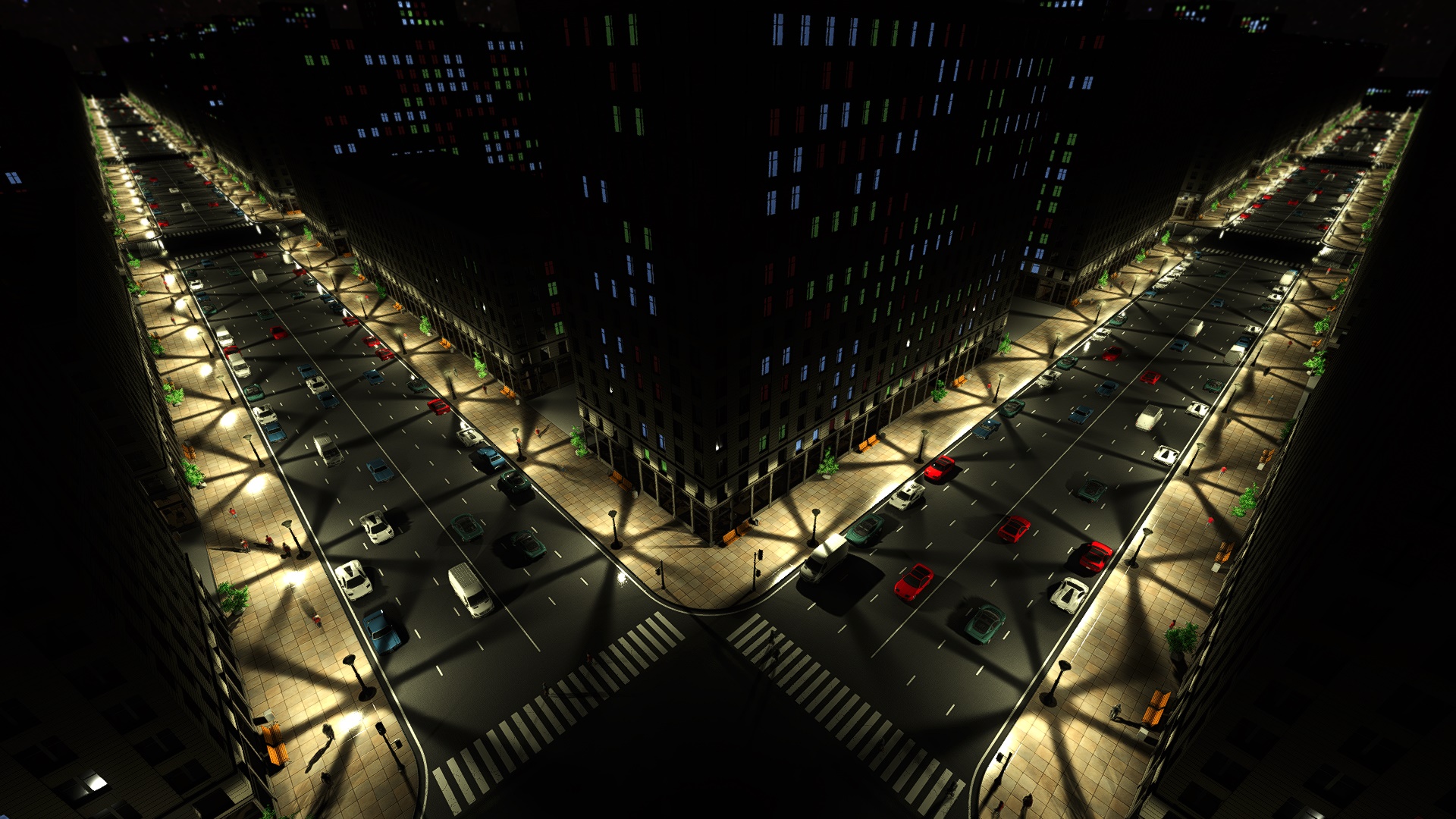
The image is good at showing the distribution of objects by distance. We are dividing the distance interval into three parts: objects near, in the middle and far. Each of part has different way to get final image on the screen.
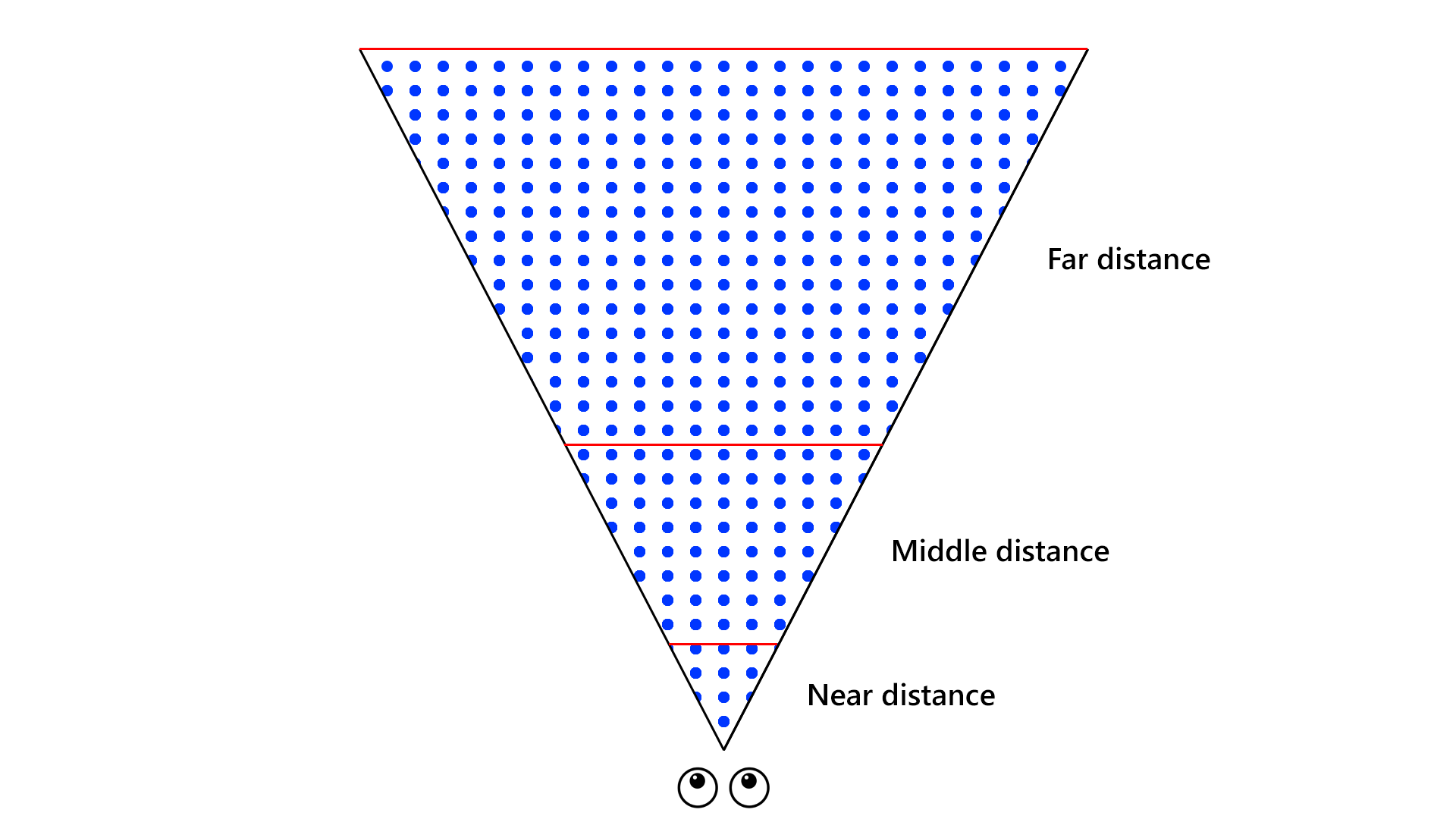
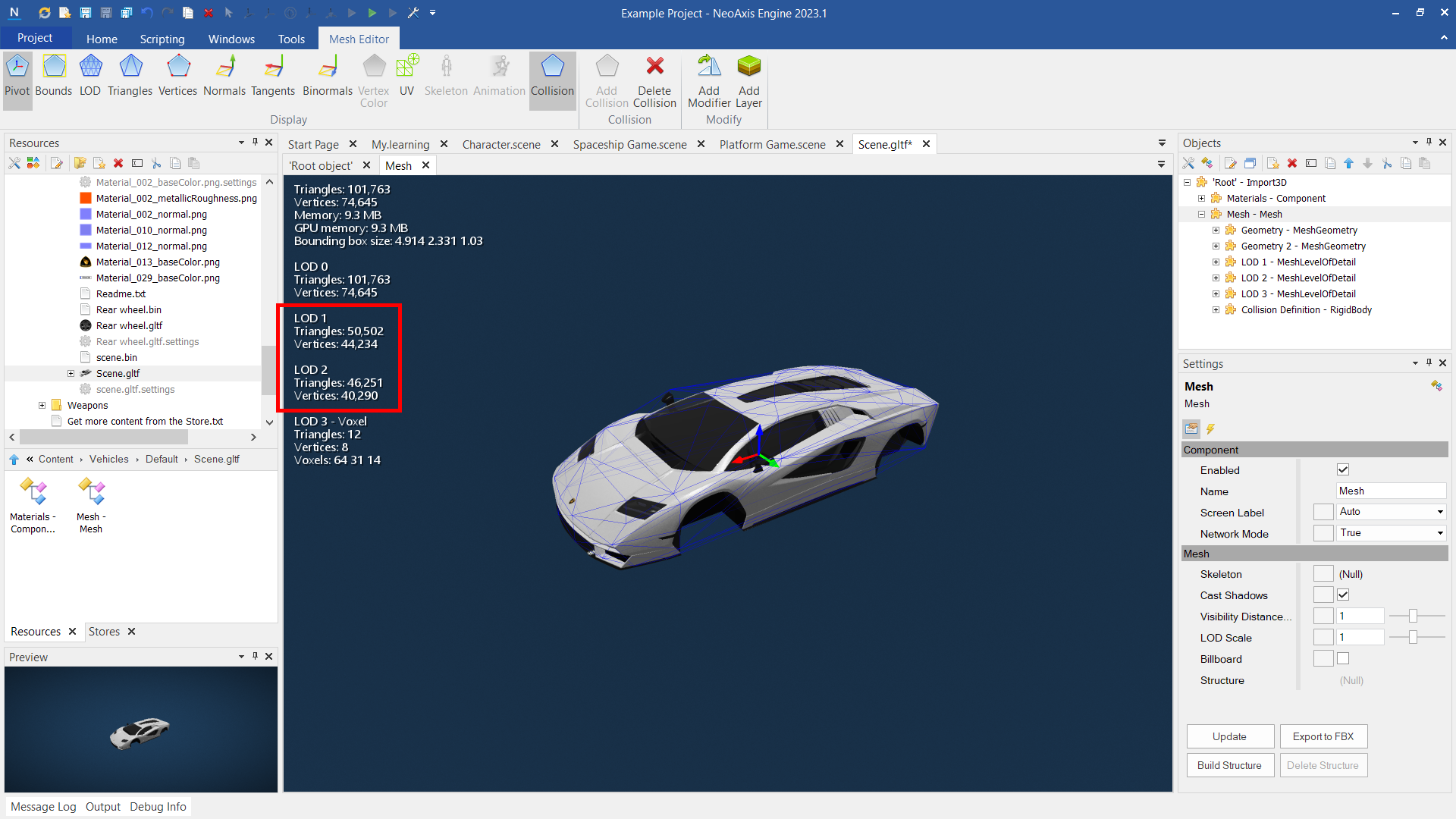
Objects at the far distance. The main problem with drawing distant objects is their large number and the number of triangles in each mesh. Usual LOD systems don't give the ability to calculate an acceptable simplified mesh, so this is a problem. The modern world requires a lot of scalability in terms of the number of objects in the scene, and all these objects are mostly at a far distance.
After a lot of experiments, we got Voxel LOD technique, which allows you to most effectively display objects at a far distance. The technique includes tools for voxelizing a mesh and a way to display a voxelized mesh. Each object in the scene is rendered using no more than 12 triangles, which solves the problem of many triangles.
In the real scene by means Voxel LOD is rendering about half pixels on the screen. Shadows and reflections are also optimized to use Voxel LOD.
Voxel LOD only visualization:
Rendering on far distance looks like this (LOD Scale = 0):

Original geometry:

Currently, at close range meshes are optimized and packed when imported, although they are drawn like regular meshes. Future engine updates will add support for mesh clustering and other optimizations. Right now at close range the fastest way is to draw the usual mesh via deferred shading.
There is an interval between near and far objects where it is inefficient to use a full mesh or Voxel LOD. On this interval we use a special LOD, which we call Careful LOD. This is the level of detail that is obtained from the original mesh, with the requirement is to reduce the number of triangles without significant visual damage. Usually 2 such levels are generated, although it is often enough to do 1 level or none.
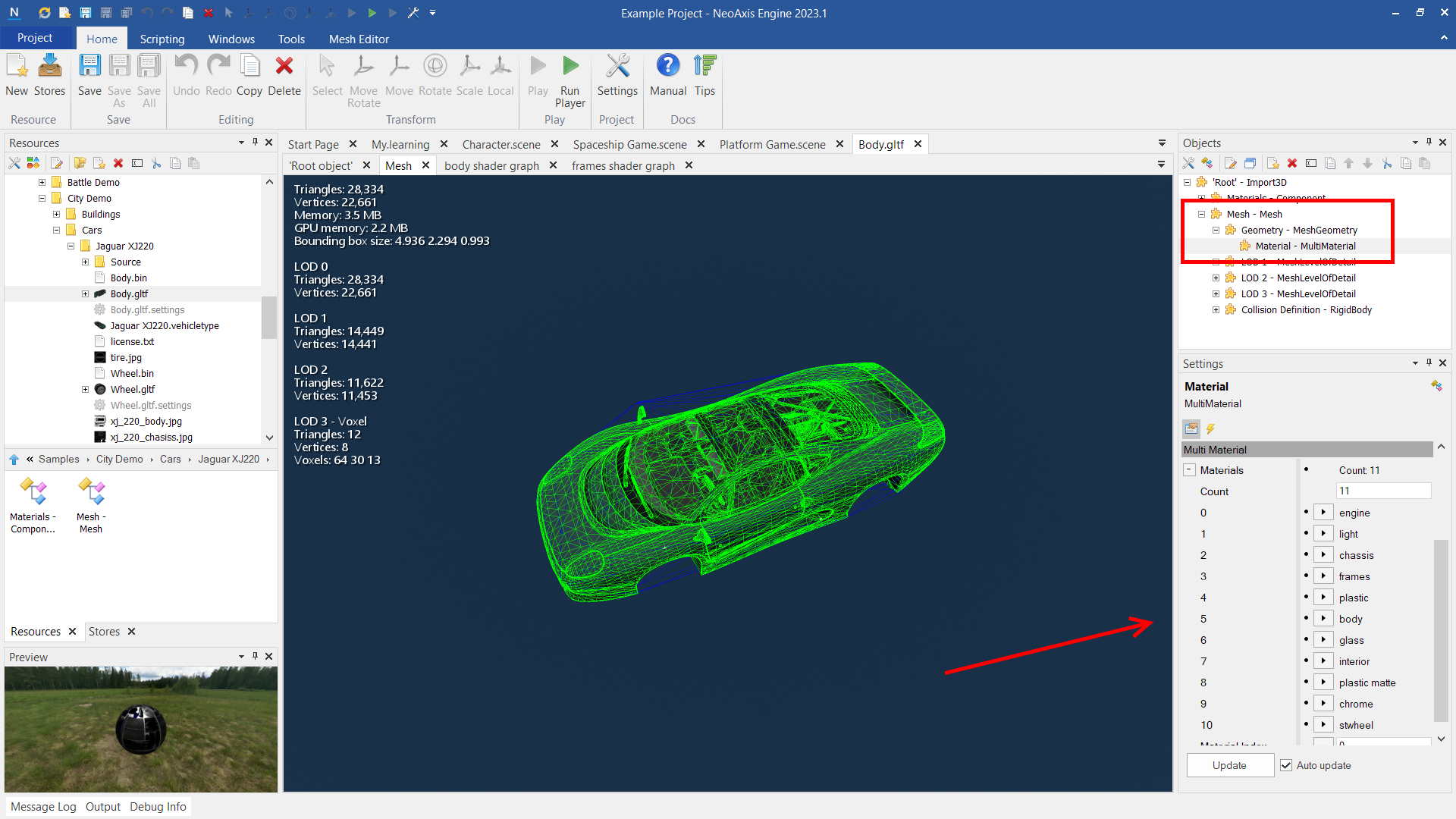
An integral part of the system is the support of multi materials. They make it possible to combine multiple materials into one draw call.
On the screenshot you can see a mesh with one mesh geometry, but with several materials.
Thanks to the static batching and automatic instancing built into the engine, the system allows you to display both static and dynamic objects very efficiently. It is enough for the developer to use the appropriate components when creating the scene, the engine will take care of the rest. Dynamic instancing uses multithreaded optimizations, which gives good scaling on multiprocessor systems.
When importing a 3D model, the system converts the channels to half or byte8 format, which reduces the size of meshes on the GPU.
The rendering pipeline of the engine splits the visible objects by distance and draws sectors from near to far. This allows to skip drawing those pixels that are not visible.
The system includes many options for customization. For example, by changing the LOD Scale you can give more quality or give more speed without changing the scene. The amount of triangles will be significantly reduced.
Transparency is fully supported. For optimization purposes, transparency for voxel LOD is implemented by using dithered alpha clip technique.
Voxel LOD transparency on far distance looks like this (LOD Scale = 0):

Original transparent materials:

Next plans are:
- Improving the system for near camera distance interval. It includes support of mesh clustering, advanced mesh packing, using cutting edge GPU features and other graphic improvements.
- Animated meshes. Voxel LOD right now not supports animated and dynamic meshes. Technically is possible to update Voxel LOD in real-time on GPU.
- Support for mobile devices.